What is Business Continuity Risk?
In today’s ever-evolving business landscape, companies face a myriad of risks that can disrupt their operations and threaten their very existence. Among these, “Business Continuity Risk” looms as a potential disruptor that demands vigilant attention. Business continuity risk refers to threats or risks that disrupt the functioning of a business. These threats maybe any untoward incidents or disasters that negatively impact an organization.

“Failing to plan is planning to fail,” Benjamin Franklin once said. This timeless wisdom underscores the importance of a Business Continuity Management Plan (BCMP), ensuring that organizations are prepared to face disruptions and continue their critical operations without missing a beat.
A study based on Mercer’s Business Responses to the COVID-19 Outbreak Survey revealed that 51 percent of organizations globally lack a business continuity plan for emergencies or disasters. This alarming statistic highlights the vulnerability of many businesses and the urgent need for comprehensive continuity planning.
In this blog, we will delve into the essential components of a BCMP and guide you through the steps to create an effective plan for your organization.
Key Takeaways (TL;DR)
- Learn how a BCMP ensures uninterrupted operations during disruptions and unexpected crises.
- Discover methods for conducting Business Impact Analysis to prioritize critical functions effectively.
- Understand strategies for risk assessment, mitigation, and integrating risk management into BCMP.
- Explore proactive and reactive continuity plans to maintain essential functions and minimize losses.
- Get insights on using VComply for automated updates, communication, and comprehensive continuity management.
Overview of Business Continuity Management Plan (BCMP)
A Business Continuity Management Plan (BCMP) is a structured approach designed to ensure that an organization’s critical operations can continue during and after a disaster or unexpected disruption.
It encompasses strategies, procedures, and resources that prepare businesses to handle potential crises, minimize their impact, and swiftly return to normal operations. The core of a BCMP is proactive planning and detailed action plans to mitigate risks and manage recovery efforts effectively.
Importance of Having a Robust BCMP
A well-structured BCMP prepares businesses to handle disruptions effectively, minimizing impact and ensuring quick recovery.
In PwC’s 2023 Global Crisis and Resilience Survey, 96% of business leaders reported experiencing disruptions in the past two years, with 76% of these disruptions having a medium to high impact on operations. This highlights the critical need for a robust BCMP.
Objectives and Goals of a BCMP
The primary objectives and goals of a Business Continuity Management Plan (BCMP) are to ensure the uninterrupted operation of critical business functions during and after a disruption.
- Protect human life and ensure safety.
- Minimize the disruption to business operations.
- Maintain customer service and company reputation.
- Safeguard organizational assets and resources.
- Ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
- Facilitate effective communication during crises.
- Establish clear recovery strategies and timelines.
Organizing a Business Continuity Team
Organizing a dedicated Business Continuity Team is vital for the effective implementation and management of a Business Continuity Management Plan (BCMP). This team ensures the efficient execution of all aspects of the BCMP, from planning and risk assessment to recovery and communication. Here’s how you can organize it:
Roles and Responsibilities of the Team
Defining clear roles and responsibilities for the Business Continuity Team is essential for the effective execution of the BCMP. Key roles include:
- Team Leader: Oversees the entire business continuity process, coordinates activities, and ensures all team members fulfill their roles.
- Risk Manager: Identifies potential risks and threats, conducts risk assessments, and develops mitigation strategies.
- Communications Coordinator: Manages internal and external communications, ensures timely updates, and maintains clear communication channels.
- Operations Manager: Ensures that critical business functions continue to operate smoothly during disruptions.
- IT Coordinator: Manages the recovery of IT systems and data, ensuring technological resilience.
- Logistics Coordinator: Handles the logistical aspects of business continuity, such as resource allocation and supply chain management.
- Compliance Officer: Ensures that all business continuity activities adhere to regulatory requirements and industry standards.
Selection Criteria for Team Members
Selecting the right team members is vital for the BCMP’s success. It includes the following criteria:
- Expertise: Knowledge and experience in risk management, business operations, and crisis management.
- Leadership Skills: Ability to lead and make decisions under pressure.
- Communication Skills: Effective in conveying information and coordinating with various stakeholders.
- Availability: Commitment to participate in planning, training, and response activities.
Establishing Clear Authority and Communication Channels
Establishing clear authority and communication channels within the Business Continuity Team is crucial for effective coordination and swift decision-making during disruptions. Here’s how you can do that:
- Define Authority Levels: Clearly outline the decision-making authority of each team member, ensuring they know when and how to escalate issues.
- Develop a Communication Plan: Create a comprehensive communication plan detailing how information will be shared within the team and with other stakeholders.
- Utilize Communication Tools: Implement reliable communication tools and platforms to facilitate real-time updates and coordination.
- Regular Meetings: Schedule regular meetings to review the BCMP, discuss potential risks, and update team members on any changes.
- Emergency Contact List: Maintain an updated list of emergency contacts for all team members and key stakeholders to ensure quick and effective communication during a crisis.
Alright, now let’s discuss the specifics of conducting a Business Impact Analysis (BIA).
Conducting a Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
Conducting a Business Impact Analysis (BIA) is essential for understanding the effects of disruptions on critical business functions. Follow these steps to conduct a BIA:
1. Specify the Purpose and Scope of BIA
A BIA identifies the critical functions and resources necessary for an organization’s survival and recovery.
- Identify Critical Functions: Determine which business functions are essential for day-to-day operations and long-term survival.
- Assess Resource Needs: Identify the resources, such as personnel, technology, and facilities, required to support critical functions.
- Evaluate Dependencies: Understand the interdependencies between various business functions and external partners.
- Define Recovery Objectives: Establish clear recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) for each critical function.
2. Methods for Identifying Critical Business Functions
Identifying critical business functions involves analyzing which activities are vital for maintaining operations and fulfilling organizational goals. You can utilize the following methods for identifying them:
- Process Mapping: Use process mapping to outline each business process and identify critical steps visually.
- Stakeholder Interviews: Conduct interviews with key stakeholders to gain insights into which functions are deemed critical.
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Distribute surveys to employees to gather information on essential business activities.
- Data Analysis: Analyze operational data to identify functions that generate the most revenue or are most frequently used.
3. Prioritizing Essential Services and Functions
Prioritizing essential services and functions ensures that the most critical areas receive attention and resources first during a disruption. Here’s how you can do it:
- Impact Assessment: Assess the impact of each function’s disruption on overall operations.
- Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs): Set RTOs to determine how quickly each function needs to be restored.
- Dependency Analysis: Identify dependencies between functions to understand which services must be restored first.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate resources to functions based on their priority and impact.
4. Analyzing Potential Impacts and Risks
Analyzing potential impacts and risks helps organizations prepare for various scenarios and develop effective response strategies. Here’s how you can do that:
- Identify Critical Processes: Determine which business processes are essential for maintaining operations.
- Evaluate Operational Impact: Assess how disruptions will affect daily operations, such as production delays or reduced service levels.
- Financial Impact Analysis: Calculate the potential financial losses from disruptions, including lost revenue, increased costs, and regulatory fines.
- Customer Impact Assessment: Analyze how disruptions will affect customer satisfaction and retention.
- Compliance and Legal Impact: Consider the implications of disruptions on regulatory compliance and legal obligations.
- Reputation Impact: Assess the potential damage to the organization’s reputation due to disruptions.
Risk Assessment and Management
Effective risk assessment and management are essential for identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats to business operations. This process ensures that organizations can anticipate risks and develop strategies to handle them efficiently. Here’s how you can do that:
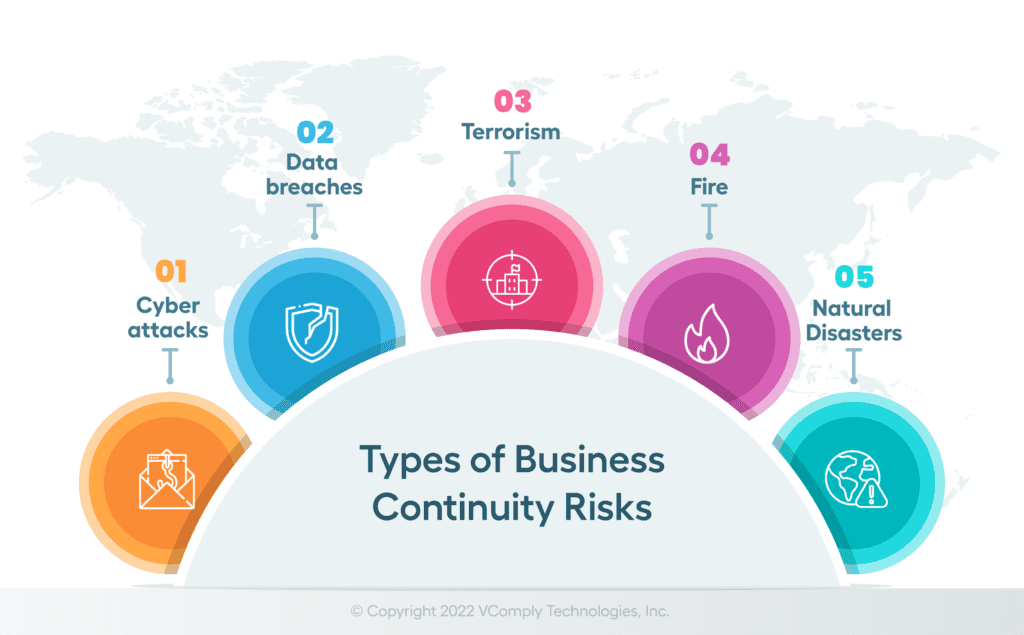
Identifying Potential Risks and Threats
The first step in risk management is identifying potential risks and threats, helping organizations understand what could disrupt their operations.
- Environmental Risks: Identify natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, and hurricanes.
- Technological Risks: Assess risks related to IT infrastructure, such as cyberattacks or system failures.
- Operational Risks: Consider risks related to day-to-day operations, such as supply chain disruptions.
- Human Risks: Identify risks associated with human factors, such as employee strikes or loss of key personnel.
- Regulatory Risks: Evaluate risks related to compliance with laws and regulations.
Assessing Vulnerabilities and Weaknesses
Organizations assess vulnerabilities and weaknesses to identify areas most susceptible to risks and needing strengthening. Here’s how you can assess them:
- Internal Audits: Conduct internal audits to identify weaknesses in current processes and controls.
- Gap Analysis: Perform a gap analysis to compare current capabilities with best practices and standards.
- Security Assessments: Conduct security assessments to identify vulnerabilities in IT systems and physical infrastructure.
- Employee Surveys: Use surveys to gather insights from employees about perceived weaknesses in operations and procedures.
- Incident Review: Review past incidents and disruptions to identify recurring vulnerabilities and areas needing improvement.
Developing Risk Mitigation Strategies
Developing risk mitigation strategies involves creating plans to reduce the impact of identified risks and enhance organizational resilience. Here’s how you can do that:
- Redundancy Planning: Implement redundancy in critical systems and processes.
- Diversification: Diversify suppliers and partners to reduce dependency on a single source.
- Training Programs: Develop training programs to improve employee readiness and response to emergencies.
- Insurance Coverage: Obtain appropriate insurance coverage to protect against financial losses from disruptions.
- Contingency Planning: Develop detailed contingency plans for different risk scenarios.
Incorporating Risk Management into the BCMP
The BCMP incorporates risk management to ensure the integration of risk mitigation strategies into the overall business continuity framework. Here’s how you can do that:
- Embed Risk Management Processes: Integrate risk assessment and management into the regular business operations and decision-making processes.
- Regular Reviews: Schedule regular reviews of risk management strategies to ensure they remain effective and relevant.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement continuous monitoring systems to detect and respond to risks in real-time.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Involve key stakeholders in risk management discussions and decisions.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation of all risk management activities and updates.
With risk management integrated, it’s time to develop effective business continuity strategies.
Developing Business Continuity Strategies
Effective business continuity strategies ensure that an organization can withstand and recover from disruptions. Here’s how you can develop them:
Creating Proactive and Reactive Strategies
Organizations create proactive and reactive strategies to minimize the impact of disruptions and maintain operations.
- Proactive Strategies: Implement measures to prevent disruptions, such as regular maintenance of critical systems and employee training. For example, in the manufacturing industry, regular equipment maintenance can prevent breakdowns.
- Reactive Strategies: Develop response plans to address disruptions when they occur. In the financial services sector, a cyberattack response plan that includes steps for isolating affected systems and communicating with stakeholders is crucial.
Different Types of Continuity Plans
Different types of continuity plans address various aspects of an organization’s operations to ensure comprehensive preparedness. Here’s what it includes:
- Operational Continuity Plans: Focus on maintaining day-to-day operations. In the healthcare industry, this includes plans for maintaining patient care services during a disaster.
- Technological Continuity Plans: Ensure the availability of IT systems and data. For higher education institutions, this involves plans for maintaining online learning platforms during campus closures.
- Economic Continuity Plans: Address financial stability and recovery. In non-profits, this might include plans for maintaining donor communications and fundraising activities during crises.
Strategies for Maintaining Essential Functions
Maintaining essential functions is critical for organizational resilience and continuity. Utilize the following strategies for maintaining them:
- Redundant Systems: Implement redundant systems to ensure critical functions can continue.
- Cross-Training Employees: Train employees to perform multiple roles to cover for absences.
- Remote Work Capabilities: Enable remote work for essential functions.
Resource Allocation and Management
Effective resource allocation and management ensure that necessary resources are available to support business continuity efforts. Here’s how you can do that:
- Prioritize Resources: Identify and prioritize critical resources needed for essential functions.
- Stockpile Essentials: Maintain a stockpile of essential supplies.
- Flexible Budgeting: Allocate budget flexibility to address unforeseen expenses.
- Collaborate with Partners: Establish agreements with suppliers and partners for resource sharing.
Creating Detailed Action Plans
Detailed action plans ensure the maintenance or quick restoration of all critical functions during a disruption. These plans provide clear, step-by-step instructions for executing business continuity strategies effectively. Here’s how you can do that:
Document Procedures for Each Critical Function
Develop step-by-step procedures for each critical function to ensure that all necessary actions are clearly outlined and can be followed efficiently during a disruption.
- Document Each Step: Write detailed steps for executing each critical function, ensuring clarity and precision.
- Use Flowcharts: Incorporate flowcharts to visualize processes and enhance understanding.
- Review and Update Regularly: Periodically review and update procedures to reflect any changes in operations or best practices.
Assign Roles and Responsibilities
Assigning defined roles and responsibilities to ensure that everyone in the team knows their specific duties during a disruption.
- Create a Responsibility Matrix: Develop a matrix to outline who is responsible for each action item.
- Communicate Expectations: Clearly communicate expectations and responsibilities to all team members.
- Ensure Redundancy: Assign backup roles to ensure continuity if a primary team member is unavailable.
Backup and Contingency Planning
Effective backup and contingency planning ensure that alternative solutions are in place to maintain critical functions when primary plans fail.
- Identify Backup Solutions: Determine backup systems and processes for each critical function.
- Develop Contingency Plans: Create plans that outline alternative actions if primary strategies are compromised.
- Test Regularly: Regularly test backup systems and contingency plans to ensure their effectiveness.
- Document Thoroughly: Keep detailed records of all backup and contingency plans for easy reference.
Emergency Response Procedures
Creating clear emergency response procedures ensures that immediate actions can be taken to protect employees, assets, and operations during a crisis.
- Outline initial actions for emergencies, such as evacuations or lockdowns.
- Define how and when to communicate with employees, stakeholders, and emergency services.
- Assign specific roles, like emergency coordinators and safety officers, to manage responses.
Communication and Coordination
Clear and consistent communication within the organization and with external stakeholders maintains order and efficiency during a disruption.
Internal and External Communication Plans
Robust internal and external communication plans keep all stakeholders informed and aligned during a disruption.
- Internal communication should focus on maintaining transparency and providing clear instructions to employees. This can include regular updates through emails, intranet posts, and team meetings.
- External communication should address customers, partners, and regulatory bodies, ensuring they are aware of the situation and any potential impacts. This can involve press releases, social media updates, and direct communications with key partners and customers.
Tools like VComply offer communication management features to aid in executing these plans efficiently.
Coordinating with Local Agencies and Partners
Establish relationships with local emergency services, government agencies, and key partners to ensure readily available support when needed. Regular meetings and collaborative planning sessions can help align expectations and resources.
Communication Templates and Tools
Standardized communication templates and tools streamline information dissemination and ensure consistency.
- Templates for emails, press releases, and social media posts can be prepared in advance to address different scenarios quickly.
- Tools such as mass notification systems, collaboration platforms (like Slack or Microsoft Teams), and crisis management software can facilitate real-time communication and coordination.
Educating and Keeping Staff Informed
Regular training sessions, workshops, and drills help employees understand their roles and responsibilities during a disruption. Keeping staff informed about updates and changes to the BCMP through regular newsletters, meetings, and an accessible intranet site ensures they are prepared and confident in their ability to respond.
Training and Testing
The effectiveness of the BCMP and staff preparedness to respond to disruptions rely on regular training and testing. It includes the following:
Developing Training Schedules and Programs
- Create regular training sessions for all employees.
- Tailor programs to different roles and responsibilities.
- Use various training methods: workshops, online courses, and drills.
- Schedule refresher courses to keep staff updated.
- Include real-life scenarios in training exercises.
Testing Different Aspects of the BCMP
- Conduct regular drills and simulations.
- Test scenarios like natural disasters, cyberattacks, and supply chain disruptions.
- Evaluate communication plans, emergency responses, and recovery strategies.
- Use tabletop exercises to test decision-making and coordination.
- Document outcomes to analyze performance.
Identifying and Addressing Plan Weaknesses
- Analyze the results of drills and simulations to find weaknesses.
- Gather feedback from participants for insights.
- Prioritize weaknesses and develop action plans.
- Implement changes based on test results.
- Schedule follow-up tests to ensure issues are resolved.
Reviewing and Updating the Plan
Regularly reviewing and updating the Business Continuity Management Plan (BCMP) is essential to ensure it remains effective and relevant.
Establishing a Schedule for Regular Reviews
A schedule for regular reviews ensures consistent monitoring and updating of the BCMP. Schedule reviews quarterly or biannually to keep the plan aligned with evolving business needs and external threats.
Methods for Updating the BCMP
Update the BCMP based on new risks and changes to maintain its effectiveness.
- Feedback Integration: Incorporate feedback from training sessions, drills, and actual incidents.
- Regulatory Updates: Ensure the BCMP complies with the latest regulatory requirements.
- Technological Advancements: Update the plan to leverage new technologies and tools.
- Industry Trends: Stay informed about industry best practices and incorporate relevant changes.
Business Continuity Management Plan – Template with Example
To help you get started with your Business Continuity Management Plan (BCMP), here is a simple template with an example for a manufacturing corporation outlining the essential sections your plan should include.
| Introduction | Purpose | Ensure continuity and resilience. |
| Scope and Objectives | Covers all departments and types of disruptions. | |
| Business Continuity Team | Team Structure and Responsibilities | Team Leader: John Doe – Oversees the entire BCMP and coordinates activities.IT Coordinator: Jane Smith – IT Coordinator: Manages recovery of IT systems and data.Operations Manager: Robert Brown – Ensures production and supply chain functions continue.Communications Coordinator: Emily White – Manages internal and external communications.Risk Manager: Michael Green – Identifies potential risks and develops mitigation strategies. |
| Business Impact Analysis (BIA) | Identification of Critical Business Functions | Production Line OperationsSupply Chain ManagementIT Systems |
| Prioritization of Essential Services | High Priority: Production line, IT systems.Medium Priority: Supply chain, customer service.Low Priority: Administrative tasks. | |
| Potential Impacts | Operational Impact: Production delays can lead to unmet customer orders.Financial Impact: Loss of revenue due to halted production.Customer Impact: Decreased customer satisfaction and potential loss of clients. | |
| Risk Assessment and Management | Identification of Potential Risks | Environmental Risks: Flooding, earthquakes.Technological Risks: Cyberattacks, system failures.Operational Risks: Equipment breakdown, supply chain disruptions. |
| Risk Mitigation Strategies | Redundancy PlanningDiversificationTraining Programs | |
| Business Continuity Strategies | Proactive Strategies | Regular maintenance,Cybersecurity measures |
| Reactive Strategies | Incident response plans | |
| Types of Continuity Plans | Operational Continuity: Maintain production and supply chain functionsTechnological Continuity: Backup IT systemsEconomic Continuity: Financial stability and recovery plans | |
| Detailed Action Plans | Step-by-Step Procedures for Critical Functions | Production Line Operations: Backup power, manual operationsIT Systems: Backup servers, system recovery |
| Backup and Contingency Plans | Supply Chain: Alternative suppliersCustomer Service: Remote work capabilities | |
| Emergency Response Procedures | Immediate Response Steps: Evacuations, communication protocolsDesignate Emergency Roles: Emergency coordinators, safety officers | |
| Communication and Coordination | Internal and External Communication Plans | Internal: Emails, intranet, team meetingsExternal: Press releases, social media updates, direct communications |
| Communication Templates and Tools | Templates: Pre-drafted emails, press releasesTools: Mass notification systems, Slack, Microsoft Teams | |
| Training and Testing | Training Schedules and Programs | Regular training sessionsTailored programs for roles |
| Testing Different Aspects of the BCMP | Drills and simulations for various scenarios | |
| Identifying and Addressing Plan Weaknesses | Analyze drill resultsGather feedbackDevelop action plansImplement changesConduct follow-up tests | |
| Reviewing and Updating the Plan | Schedule for Regular Reviews | Quarterly and biannual reviews |
| Methods for Updating the BCMP | Feedback IntegrationRegulatory UpdatesTechnological AdvancementsIndustry Trends |
Case Study: Karmak’s BCM Response to a Ransomware Attack

In February 2023, Karmak, a technology solutions provider for the trucking industry, successfully navigated a ransomware attack due to its robust Business Continuity Management (BCM) framework.
The company’s BCM strategy included thorough risk assessments, a detailed disaster response plan, clear communication lines, and regular continuity testing.
When the attack occurred, these measures enabled Karmak to swiftly contain the ransomware, preventing significant operational disruptions and ensuring minimal downtime. As a result, the company maintained service continuity for its clients despite the cyberattack.
This case study highlights the importance of comprehensive BCM planning to mitigate risks and enhance organizational resilience in the face of unexpected challenges.
Conclusion
Having a well-crafted Business Continuity Management Plan (BCMP) is indispensable for ensuring that your organization remains resilient and operational during disruptions. By systematically planning, organizing a dedicated team, conducting thorough impact analyses, managing risks, and developing comprehensive strategies, businesses can effectively safeguard their operations and assets.
To simplify and streamline this process, VComply offers comprehensive solutions for creating, managing, and updating your business continuity plans, ensuring that you are always prepared for any eventuality. With features like automated workflows, real-time updates, and detailed reporting, VComply helps you stay ahead of potential disruptions and maintain business continuity.
Take the proactive step to protect your organization today. Try VComply by requesting a free demo Now!
